今天继续stl的简单应用
1.CF4C Registration system
题目描述
题目背景
一个名为 “Berlanddesk” 的电子邮件系统即将在 Berland 上线运营。该电子邮件系统的管理员希望整个系统的建设可以尽早完成,因此他们找到了资深程序员您,希望您能够为他们开发一个用户注册系统的原型产品。
该系统的运行遵循以下原则:
新用户注册时,他将向系统发送一则内容为其用户名的请求,如果该用户名尚未存在于系统数据库内,则将该用户名插入数据库,同时用户得到回应信息 OK 表示其已经成功注册。如果用户请求的用户名已经存在于数据库内,那么系统将产生一个新的用户名并将其加入数据库。新用户名由用户请求的用户名与正整数 $i$ 构成,$i$ 为使 “用户名i” 尚未存在于数据库内的最小的 $i$。
输入格式
第一行一个整数 $n(1 \le n \le 10^5)$。接下来 $n$ 行,每行表示用户向系统发出的一则请求。每行内容均非空且均为由至多 $32$ 个小写拉丁字母组成的字符串。
输出格式
$n$ 行,每行表示系统对一则请求做出的回应。如果该用户名尚未存在于系统数据库内,则输出 OK 。如果用户请求的用户名已经被注册,则输出依照规则生成的新用户名。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 4 |
输出 #1
1 | OK |
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
1 | 6 |
输出 #2
1 | OK |
今日题解
大体思路是set保存一份原始的,map记录出现次数。
1 |
|
2.CF69E Subsegments
题目描述
Programmer Sasha has recently begun to study data structures. His coach Stas told him to solve the problem of finding a minimum on the segment of the array in 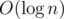
输入格式
The first line contains two positive integers $ n $ and $ k $ ( $ 1<=n<=10^{5},1<=k<=n $ ) — the number of array elements and the length of the segment.
Then follow $ n $ lines: the $ i $ -th one contains a single number $ a_{i} $ ( $ -10^{9}<=a_{i}<=10^{9} $ ).
输出格式
Print $ n–k+1 $ numbers, one per line: on the $ i $ -th line print of the maximum number of those numbers from the subarray $ a_{i} $ $ a_{i+1} $ … $ a_{i+k-1} $ that occur in this subarray exactly 1 time. If there are no such numbers in this subarray, print “Nothing”.
题意翻译
对于固定长度的每个数列,Sasha必须找到在给定数列上出现的元素的最大值。帮Sasha解决这个问题。
第一行两个整数n 和k (1≤n≤105,1≤k≤n),表示数组元素的数目和数列的长度。
然后 n 行,第 i 行包含一个数字a**i(−109≤a**i≤109)
输出 n−k+1 个数,每行输出一个数,第i行输出以为i为起点,长度为k的数列中的最大值。
并且在aia**i+1…..a**i+k−1,中每个数只能出现一次(重复视为没有元素),如果数列中没有元素,输出Nothing。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 5 3 |
输出 #1
1 | 1 |
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
1 | 6 4 |
输出 #2
1 | 4 |
今日题解:
写了两份,一份是暴力,一份是滑动窗口
暴力:
1 |
|
滑动窗口:
1 |
|
3.CF78A Haiku
题目描述
Haiku is a genre of Japanese traditional poetry.
A haiku poem consists of 17 syllables split into three phrases, containing 5, 7 and 5 syllables correspondingly (the first phrase should contain exactly 5 syllables, the second phrase should contain exactly 7 syllables, and the third phrase should contain exactly 5 syllables). A haiku masterpiece contains a description of a moment in those three phrases. Every word is important in a small poem, which is why haiku are rich with symbols. Each word has a special meaning, a special role. The main principle of haiku is to say much using a few words.
To simplify the matter, in the given problem we will consider that the number of syllable in the phrase is equal to the number of vowel letters there. Only the following letters are regarded as vowel letters: “a”, “e”, “i”, “o” and “u”.
Three phases from a certain poem are given. Determine whether it is haiku or not.
输入格式
The input data consists of three lines. The length of each line is between $ 1 $ and $ 100 $ , inclusive. The $ i $ -th line contains the $ i $ -th phrase of the poem. Each phrase consists of one or more words, which are separated by one or more spaces. A word is a non-empty sequence of lowercase Latin letters. Leading and/or trailing spaces in phrases are allowed. Every phrase has at least one non-space character. See the example for clarification.
输出格式
Print “YES” (without the quotes) if the poem is a haiku. Otherwise, print “NO” (also without the quotes).
题意翻译
题目大意:
Haiku是日本传统诗歌的一种流派。
这种诗歌由三个短句组成,共有17个音节。
其中,第一个短句有5个音节,第二个短句有7个音节,第三个短句有5个音节。
为了简化问题,短句的音节数视为这个短句中的元音字母数。
只有以下字母被视为元音字母:“a”,“e”,“i”,“o”和“u”。
任务:给出一首诗,判断它是不是Haiku。
INPUT:
输入数据由三行组成。每行长度在1~100之间,由小写英文字母组成。允许有空格前缀或空格后缀。每个短句中至少有一个小写字母。
OUTPUT:
如果这首诗是Haiku,输出“YES”,否则输出“NO”。
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | on codeforces |
输出 #1
1 | YES |
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
1 | how many gallons |
输出 #2
1 | NO |
今天题解:
水题,考察getline的使用:getline(cin, 变量)
1 |
|
4.CF799B T-shirt buying
题目描述
A new pack of $ n $ t-shirts came to a shop. Each of the t-shirts is characterized by three integers $ p_{i} $ , $ a_{i} $ and $ b_{i} $ , where $ p_{i} $ is the price of the $ i $ -th t-shirt, $ a_{i} $ is front color of the $ i $ -th t-shirt and $ b_{i} $ is back color of the $ i $ -th t-shirt. All values $ p_{i} $ are distinct, and values $ a_{i} $ and $ b_{i} $ are integers from $ 1 $ to $ 3 $ .
$ m $ buyers will come to the shop. Each of them wants to buy exactly one t-shirt. For the $ j $ -th buyer we know his favorite color $ c_{j} $ .
A buyer agrees to buy a t-shirt, if at least one side (front or back) is painted in his favorite color. Among all t-shirts that have colors acceptable to this buyer he will choose the cheapest one. If there are no such t-shirts, the buyer won’t buy anything. Assume that the buyers come one by one, and each buyer is served only after the previous one is served.
You are to compute the prices each buyer will pay for t-shirts.
输入格式
The first line contains single integer $ n $ ( $ 1<=n<=200000 $ ) — the number of t-shirts.
The following line contains sequence of integers $ p_{1},p_{2},…,p_{n} $ ( $ 1<=p_{i}<=1000000000 $ ), where $ p_{i} $ equals to the price of the $ i $ -th t-shirt.
The following line contains sequence of integers $ a_{1},a_{2},…,a_{n} $ ( $ 1<=a_{i}<=3 $ ), where $ a_{i} $ equals to the front color of the $ i $ -th t-shirt.
The following line contains sequence of integers $ b_{1},b_{2},…,b_{n} $ ( $ 1<=b_{i}<=3 $ ), where $ b_{i} $ equals to the back color of the $ i $ -th t-shirt.
The next line contains single integer $ m $ ( $ 1<=m<=200000 $ ) — the number of buyers.
The following line contains sequence $ c_{1},c_{2},…,c_{m} $ ( $ 1<=c_{j}<=3 $ ), where $ c_{j} $ equals to the favorite color of the $ j $ -th buyer. The buyers will come to the shop in the order they are given in the input. Each buyer is served only after the previous one is served.
输出格式
Print to the first line $ m $ integers — the $ j $ -th integer should be equal to the price of the t-shirt which the $ j $ -th buyer will buy. If the $ j $ -th buyer won’t buy anything, print -1.
输入输出样例 #1
输入 #1
1 | 5 |
输出 #1
1 | 200 400 300 500 911 -1 |
输入输出样例 #2
输入 #2
1 | 2 |
输出 #2
1 | 1 1000000000 |
今日题解:
我只想到暴力实现,看题解尝试写出优先队列的实现方式。
暴力:
1 |
|
优先队列版:
1 |
|
总结
第一题考察map的使用,第二题考察滑动窗口。




